Adopting a low-carb diet within a vegan lifestyle may seem challenging at first—but when combined with a focus on high-quality protein, it can deliver numerous health benefits. Whether your goal is weight loss, lowering blood pressure, or simply embracing a plant-based diet that meets all your nutritional needs.
This guide will walk you through the key concepts, science, and strategies for making a low carbohydrate diet both enjoyable and effective. By carefully planning your vegan meal plan and incorporating essential ingredients like chia seeds, hemp seeds, olive oil, and soy milk, you can ensure you get enough protein and essential nutrients without relying on animal products.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explain the fundamentals of a low-carb vegan approach, delve into the science behind high protein vegan diets, and provide actionable tips for meal planning and lifestyle integration. Whether you’re interested in the vegan keto diet or simply want to cut down on grams of carbs while maintaining a vegan lifestyle, read on for good news about how careful planning can lead to a balanced, flavorful eating pattern.
Understanding the Low Carb Vegan Diet
What is a Low-Carb Diet?
A low-carb diet emphasizes reducing the intake of carbohydrates—primarily found in whole grains, starchy vegetables, and sugars—to help with weight loss and stabilize blood sugar levels. This type of low carbohydrate diet encourages your body to rely more on fats for energy, which is the principle behind the ketogenic diet. By limiting carbs, or eating a lower carb diet, you can help improve your body weight management and reduce the risk of heart disease.
The Vegan Lifestyle and Plant-Based Diet
Embracing a vegan lifestyle means eliminating all animal products from your diet. Instead, you focus on a plant-based diet rich in fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and seeds. This approach not only promotes ethical and animal welfare benefits but also offers a diverse array of nutrients. When combined with a low-carb plan, it becomes a powerful strategy for weight loss and reducing blood sugar and blood pressure.
Health Benefits of a Low-Carbohydrate Diet
The benefits of reducing your carbohydrate intake are well documented. A low-carb diet can lead to improvements in hdl cholesterol, reduce fewer calories intake overall, and support weight loss by helping regulate carbohydrate intake and stabilize blood sugar levels. This kind of dietary pattern is also associated with a lower risk of chronic conditions such as heart disease and metabolic disorders.
Low Carb Vegan Diet Recipes
Discover our collection of low-carb vegan recipes that work perfectly for anyone following a low carb diet. When looking for a low carb meal, you do not have to sacrifice flavour. I hope that you enjoy my low carb recipes below.
The Science Behind High Protein Vegan Diets
Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues, supporting a strong immune system, and promoting muscle repair—all while helping you feel full and satisfied. But without animal protein, many wonder if a vegetarian diet or vegan diet can truly deliver a great source of protein. The answer lies in the quality and planning of plant-based proteins.
Importance of High-Quality Protein
High-quality protein sources are those that contain all the essential amino acids—the building blocks that your body cannot produce on its own. For active individuals or those on a vegan meal plan aiming for weight loss, ensuring you get enough protein is key. Recent research has shown that when protein intake is matched, both omnivorous and vegan diets can support comparable muscle protein synthesis rates. For example, a randomized controlled trial demonstrated that the daily myofibrillar protein synthesis (MyoPS) rates in individuals consuming a high-protein vegan diet were similar to those on an omnivorous diet.
Essential Amino Acids and Complete Protein Sources
Not every protein is the same. Complete proteins contain all nine essential amino acids in sufficient quantities. Although many plant-based foods are naturally lower in one or more of these amino acids, combining them—such as pairing legumes with whole grains or nut butters—can yield a complete amino acid profile. For more detailed insights on how vegans can achieve complete protein intake from plant-based foods, check out this comprehensive review:
Comparing Plant-Based Proteins and Animal Protein
Historically, animal protein has been regarded as the gold standard for protein quality due to its complete amino acid profile. However, emerging studies indicate that with careful planning and by using a variety of plant-based proteins like soy protein, hemp seeds, and nutritional yeast, vegans can match the protein quality traditionally found in dairy products and other animal sources. Research highlighted by Massachusetts General Hospital underscores that the nutritional benefits of plant-based proteins can be equivalent to animal proteins when consumed as part of a well-planned vegan meal plan.
Comparison Chart For Vegan Foods With High Protein Low Carb Ratio
| Food Item | Protein (g/100g) | Carbs (g/100g) or Net Carbs | Protein/Carb Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soy Protein Isolate (Powder) | ~90 | ~2 | ~45 |
| Pea Protein Isolate (Powder) | ~80 | ~3 | ~27 |
| Firm Tofu | ~10 | ~2 | 5 |
| Hemp Seeds | ~31 | ~9 | ~3.4 |
| Spirulina | ~57 | ~24 | ~2.4 |
| Tempeh | ~19 | ~9 | ~2.1 |
| Chia Seeds (Net Carbs) | ~17 | ~8 | ~2.1 |
| Pumpkin Seeds (Net Carbs) | ~19 | ~10 | ~1.9 |
| Seitan | ~25 | ~14 | ~1.8 |
| Almonds (Net Carbs*) | ~21 | ~12 | ~1.75 |
| Nutritional Yeast | ~50 | ~35 | ~1.4 |
| Edamame (boiled) | ~11 | ~8 | ~1.38 |
*Net carbs for almonds are calculated by subtracting fiber from total carbs.
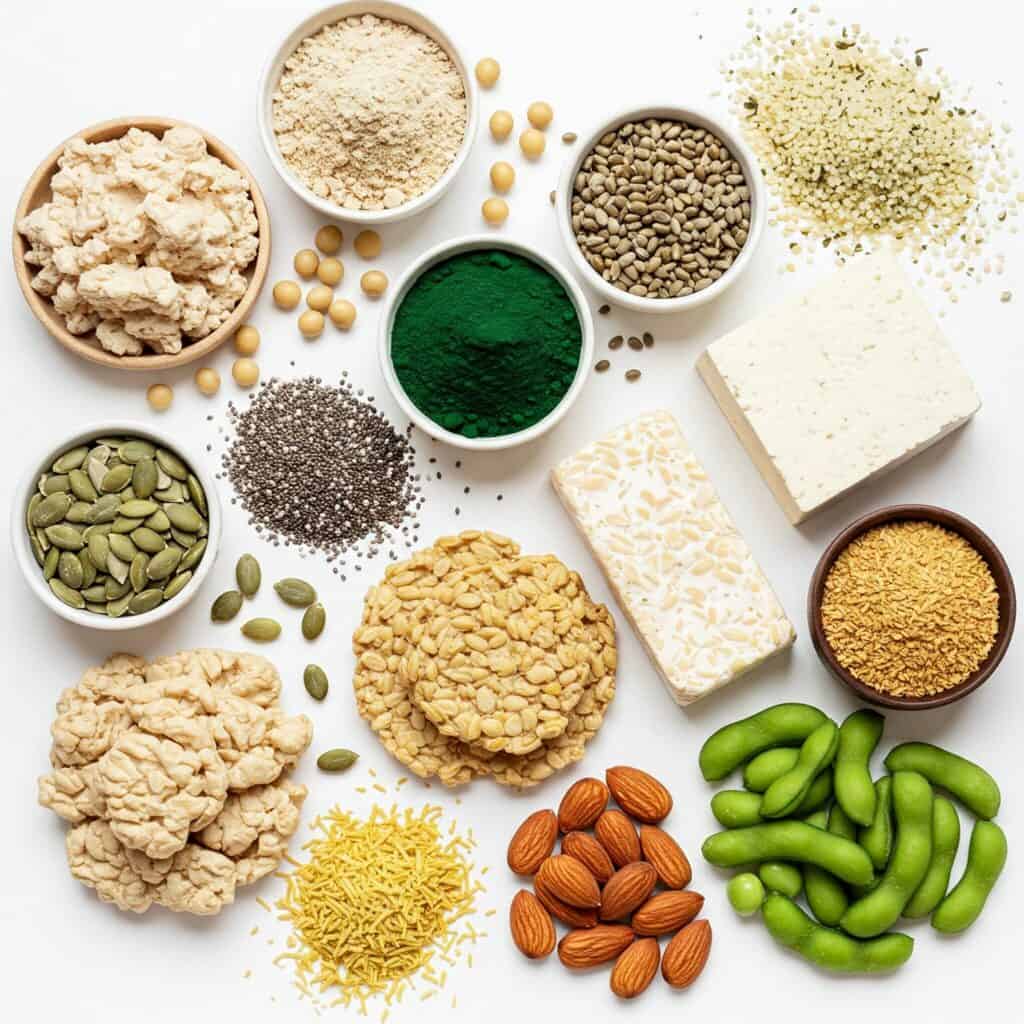

Key Ingredients for Low Carb Vegan Diets
Super Seeds: Chia, Hemp, Pumpkin, and Sesame Seeds
Seeds like chia seeds, hemp seeds, pumpkin seeds, and sesame seeds are nutritional powerhouses. They offer healthy fats, essential nutrients, and high-quality protein in small portions, making them perfect for keeping your grams of carbs low while ensuring you get enough protein.
Nut Butters and Dairy Alternatives
Nut butters, particularly peanut butter and seed butter, are excellent sources of plant-based proteins and healthy fats. Paired with dairy alternatives like soy milk or coconut milk, these ingredients help you create creamy textures and add a boost of essential nutrients without the need for traditional dairy products.
Healthy Fats and Oils
Fats are an integral part of any balanced diet. In a low-carb diet, incorporating healthy fats is vital for satiety and energy. Ingredients such as olive oil, coconut oil, and avocado oil provide your body with fatty acids necessary for various functions while enhancing the flavor of your dishes. Including sources of macadamia nuts and nutritional yeast can also add both texture and nutritional benefits.
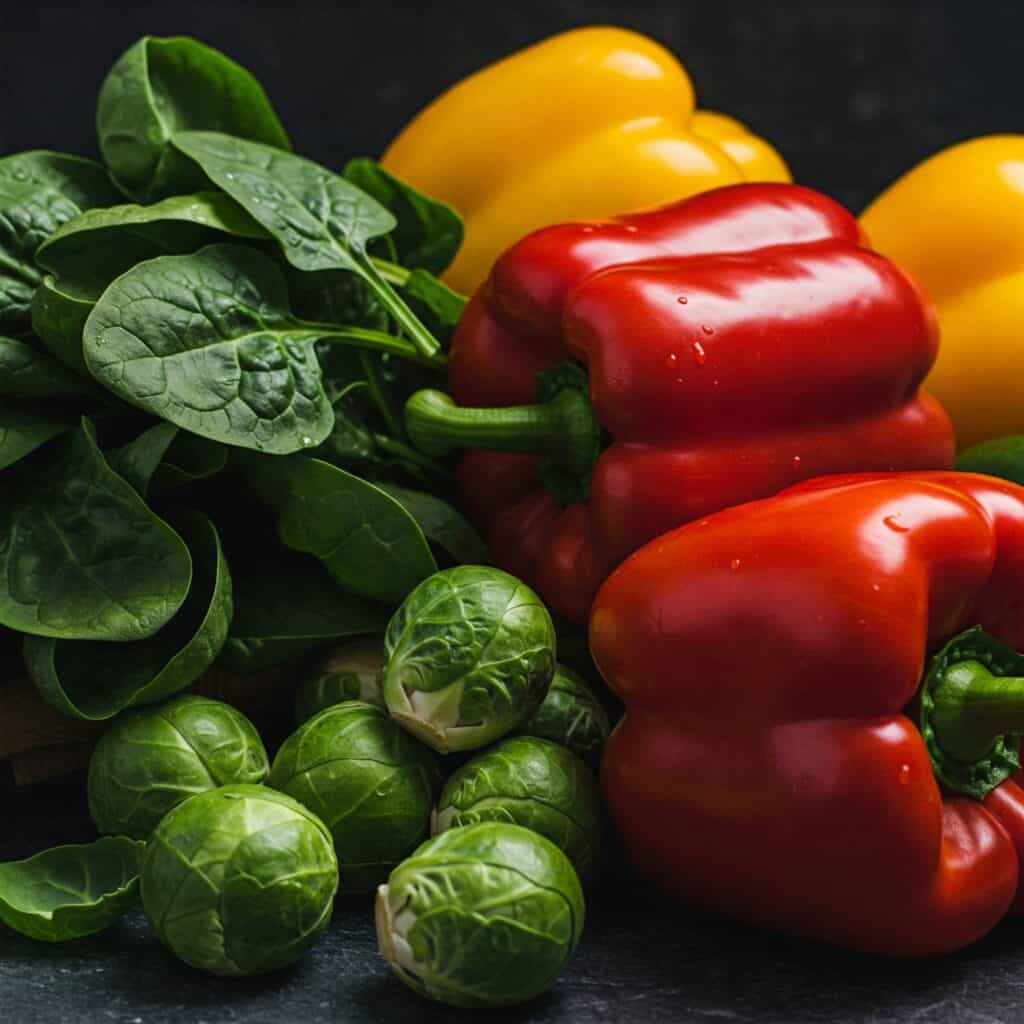
Low-Carb Vegetables and Fruits
Focus on non-starchy vegetables and leafy greens like spinach, bell peppers, and cruciferous vegetables such as brussels sprouts and red pepper. These foods are low in grams of carbs yet high in important vitamins like vitamin C and vitamin B. They help maintain overall health and support weight loss and improved blood sugar control.

Planning Your Low Carb Vegan Meal Plan
A well-structured meal plan is crucial to the success of any low-carb vegan diet. Here are some strategies to keep you on track:
Calculating Carbohydrate Intake and Grams of Net Carbs
Monitoring your carbohydrate intake is essential for maintaining a low-carb diet. Be mindful of the grams of net carbs in your meals by prioritizing non-starchy vegetables over whole grains. Tools such as food scales and nutrition tracking apps can help you measure your portions accurately.
Balancing Nutritional Needs and Dietary Patterns
Achieving a balanced vegetarian diet means incorporating a mix of plant-based proteins, healthy fats, and essential nutrients. Whether you’re using soy products, coconut milk, or olive oil, focus on diversifying your protein sources to ensure you obtain a full spectrum of essential amino acids.
Tips for Weight Loss and Managing Body Weight
Combining a low-carb diet with careful planning and mindful eating habits can facilitate weight loss without sacrificing taste or nutritional value. Opt for meals that provide fewer calories while still delivering high-quality protein and essential fatty acids. Consider how salad dressings and a green smoothie can be creatively used to enhance flavor without adding excessive carbs.
Integrating a Vegan Lifestyle with a Low-Carb Diet
Transitioning to a low-carb vegan diet may require some adjustments, especially if you’re accustomed to a high-carb vegan diet. Here are some tips for a smooth transition:
Transitioning from a High-Carb Vegan Diet
If you’re moving away from a high-carb vegan diet, gradually reduce your intake of whole grains and replace them with non-starchy vegetables and other low-carb options. This gradual shift can help your body adapt without compromising your nutritional status.
Incorporating Whole Grains and Vegan Foods in Moderation
While many plant-based foods are beneficial, it’s important to consume whole grains in moderation when following a low-carbohydrate diet. Balance is key—include leafy greens and non-starchy vegetables to keep your grams of carbs low while still enjoying the nutritional benefits of grains.
Benefits for Heart Disease, Blood Pressure, and Health Conditions
A low-carb vegan diet may also contribute to reduced risks of heart disease and improved blood pressure control. The emphasis on plant-based proteins and healthy fats—like those found in olive oil and coconut oil—can help lower cholesterol levels and promote better cardiovascular health. For individuals with existing health conditions, consulting with a healthcare provider is a good idea to tailor the diet to your specific needs.
Lifestyle Factors for Success
Beyond your food choices, several lifestyle factors can influence your success on a low-carb vegan diet.
Impact on Blood Sugar, HDL Cholesterol, and Fatty Acids
Adopting this eating pattern can help stabilize your blood sugar levels and improve your hdl cholesterol profile. By focusing on plant-based proteins and healthy fats, you support your body’s overall metabolic health and enhance its ability to manage energy efficiently.
Role of Herbal Teas and Black Coffee
Beverages such as herbal teas and black coffee can complement your meal plan by providing a low-calorie boost of antioxidants without disrupting your low-carb goals. They can also serve as alternatives to sugary drinks, further helping with weight loss and blood sugar regulation.

Addressing Common Health Concerns
Changing your eating habits can sometimes bring up concerns, especially when managing health conditions.
Managing Health Conditions with Plant-Based Foods
Many individuals turn to a plant-based diet to mitigate conditions like high blood pressure and heart disease. Incorporating a variety of vegan foods ensures you get the essential nutrients needed to support your body’s functions while avoiding the negative aspects often associated with animal sources.
The Role of a Healthcare Provider in Your Vegan Meal Plan
It’s always wise to consult with a healthcare provider when making significant dietary changes. They can help you tailor your vegan meal plan to meet your nutritional needs, ensuring you receive a balance of complete proteins, healthy fats, and other key nutrients. This collaborative approach can help address any concerns regarding body weight, blood pressure, or other health conditions.
The Long Term Impact: Studies and Clinical Trials
Long-term adherence to a low-carb vegan diet can yield significant benefits. Recent clinical trials and systematic reviews have shed light on how such diets impact overall health over extended periods.
Insights from Recent Clinical Trials and Systematic Reviews
Several studies have explored the long-term effects of high-protein vegan diets. For instance, systematic reviews of clinical trials indicate that when vegans consume adequate grams of protein from diverse plant-based proteins, they experience similar muscle protein synthesis rates and improvements in body weight and metabolic health compared to omnivores. These findings highlight that with careful planning and adherence to balanced dietary patterns, a vegan lifestyle can support long term health goals and reduce the risk of heart disease. Additionally, reviews published in reputable journals underline that switching from a high-carb vegan diet to one that prioritizes low-carb recipes and vegan keto diet principles may further enhance these benefits.
Long Term Versus Short Term Benefits
In the short term, you might notice improvements in blood sugar, blood pressure, and weight loss. Over the long term, maintaining a low carbohydrate diet that is rich in plant-based proteins has been associated with reduced risks of chronic diseases and improved overall health conditions. The emerging research is promising and suggests that this approach not only meets immediate nutritional needs but also supports sustainable, healthy eating habits over time.
Conclusion: Low Carb Vegan Diet
Embracing a low carb vegan diet doesn’t mean sacrificing flavor, nutrition, or high-quality protein. With a well-planned approach that includes a diverse range of plant-based proteins, healthy fats, and non-starchy vegetables, you can create meals that support weight loss, improve blood sugar control, and lower the risk of chronic health conditions such as heart disease.
Whether you’re following a vegan keto diet or simply transitioning from a high-carb vegan diet, this guide provides the good news: with careful planning and a focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods, you can enjoy a balanced, satisfying diet that meets all your nutritional needs.
There are a lot of healthy dinner recipes that feature healthy carbs, and by incorporating more plant-based protein options – like tofu scramble made with a block of tofu you will feel full and satisfied.
If you are craving a pasta dish substitute the noodles with spaghetti squash or even try using zucchini noodles. I hope you enjoy these delicious recipes. To add an additional protein source to my cucumber salad recipes, you can add in my vegan tofu cheese.
By incorporating key ingredients like chia seeds, hemp seeds, olive oil, and coconut milk into your vegan meal plan, and by understanding the science behind high protein vegan diets—supported by recent clinical trials and systematic reviews—you can confidently maintain a diet that fuels your body, supports muscle repair with complete protein sources, and promotes overall well-being in both the short term and long term.
Low-Carb Vegan Diet FAQs
Focus on including:
- Tofu and tempeh
- Soy milk
- Chia seeds
- Hemp seeds
Combine different sources throughout the day for complete protein.
A complete protein contains all nine essential amino acids. Plant-based complete proteins include:
- Quinoa
- Buckwheat
- Soy products
Yes. Research shows comparable muscle protein synthesis rates when protein intake is matched. Reference study:
- Non-starchy vegetables
- Leafy greens
- Chia seeds
- Healthy fats (olive oil, coconut milk)
Not necessary. Focus on variety throughout the day. Helpful combinations:
- Legumes + grains
- Nuts + whole grains
References For Low Carb Vegan Diets
Daily MyoPS Rates in Omnivorous vs. Vegan Diets:
PubMed study on MyoPS rates
Cardiometabolic Effects in Identical Twins:
JAMA Network Open – Cardiometabolic Effects of Omnivorous vs. Vegan Diets in Identical Twins
Complete Protein for Vegans – Overview and Insights:
Healthline’s Comprehensive Guide
Plant-Based Proteins Spotlight:
Massachusetts General Hospital’s Article










