Ever stood in the grocery store, staring at labels like “plant-based,” “vegan,” or “vegetarian,” and wondered, “What’s the actual difference?” You’re not alone! These terms are often used interchangeably, but they’re not the same. Let’s break it down—no jargon, just clarity.
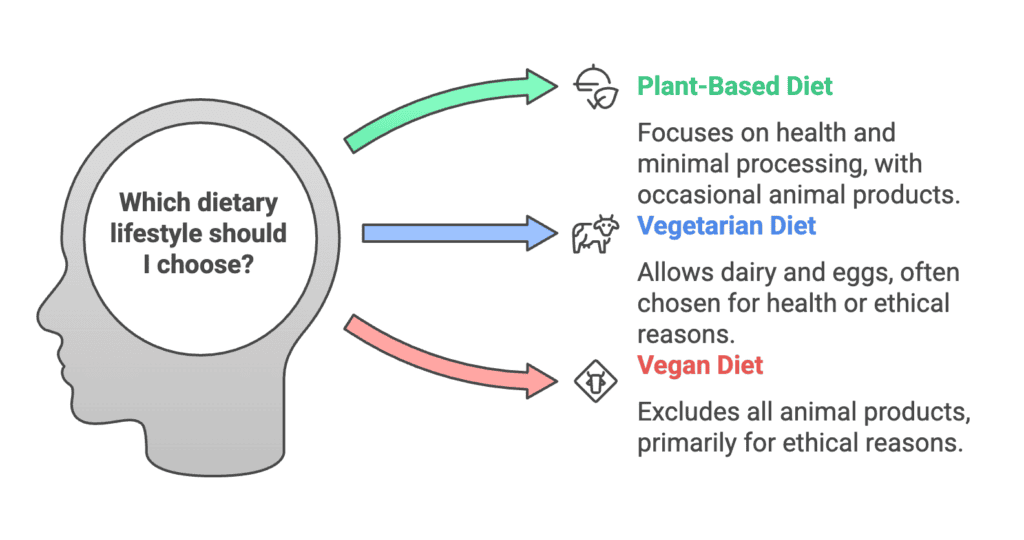
Plant-Based Diet: Flexibility Meets Focus on Plants
A plant-based diet is like a choose-your-own-adventure book. It’s centered on plant foods—think veggies, fruits, legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds—but doesn’t always exclude animal-derived foods. Some people on this diet might enjoy occasional fish, eggs, or even a burger while keeping plants as the star of their plate.
Wait—can you eat fish on a plant-based diet?
Yes and no. Definitions vary:
- Strict plant-based purists: Avoid all animal products, including fish (similar to veganism).
- Flexible plant-based eaters: Prioritize plants but may include fish occasionally for its omega-3 fatty acids or protein.
Why the confusion? The term “plant-based” isn’t regulated, so interpretations differ. For clarity, always ask: “Is this diet 100% plants, or is there flexibility?”
Key Features:
- Primary focus: Minimally processed plant-based foods (e.g., brown rice, lentils, fresh fruits).
- Flexibility: May include small amounts of fish, eggs, or dairy.
- Health angle: Often adopted for lower risk of heart disease, weight loss, or environmental impact.
Did you know? The Mediterranean diet—packed with olive oil, veggies, and fish—is considered plant-based! It’s linked to heart health, human health, and longevity, thanks to its wide variety of foods like plant-rich diets and healthy fats.
Vegetarian Diet: Meat-Free, But Not Always Dairy-Free
Vegetarians skip meat products but often embrace dairy foods, eggs, and honey. It’s like saying, “I’ll pass on the steak, but yes to cheese pizza!” There are different types of vegetarian diets:
- Lacto-ovo: Eats dairy and eggs (the most common).
- Pescatarian: Adds fish and seafood (Note: Some argue pescatarians aren’t “true” vegetarians).
- Flexitarian diet: Mostly plants with occasional meat.

Health Perks:
- Lower BMI and reduced risk of cardiovascular disease compared to omnivorous diets.
- The health benefits of a vegetarian diet include better heart health and a balanced diet, but watch out for potential gaps in vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids (found in animal sources).
Pro tip: Pair plant sources of iron (like spinach) with vitamin C (citrus fruits) to boost absorption.
Vegan Diet: Ethics Meet Exclusion
Veganism isn’t just a diet—it’s a lifestyle. Ethical reasons and environmental reasons drive most vegans to avoid animal-derived products entirely, from food to clothing. Founded by Donald Watson in 1944, veganism rejects animal welfare harms in industries like dairy, fishing, and cosmetics.
What’s Off the Table?
- Animal-based foods: Meat, dairy, eggs, honey, fish.
- Animal by-products: Leather, wool, gelatin.

Health Considerations:
- Vegan diets can be rich in dietary fiber and plant-based protein (tofu, lentils), but require careful planning to get enough protein and essential nutrients like vitamin B12.
- Supplements like vitamin D or fortified vegan food (e.g., plant-based milks) are often needed.
Fun fact: Oat milk and almond milk are booming as plant-based alternatives to dairy, and innovative meat substitutes like plant-based meat make transitioning easier!
Plant-Based vs Vegan: The Big Debate
1. Ethics vs. Health
- Vegans avoid animal exploitation for ethical reasons, while plant-based eaters often prioritize human health or environmental impact (some still eat fish or eggs).
2. Flexibility
- A vegan lifestyle is strict—no leather jackets, honey, or fish.
- Plant-based focuses on diet, allowing occasional animal-based products (if desired), making it closer to a flexitarian diet.
3. Nutritional Needs
- Both diets require planning to meet nutrient needs like vitamin B12, iron, and calcium.
- Vegans might rely on nutritional yeast or fortified plant-based milks; plant-based eaters may get essential nutrients from fish, eggs, or milk products.
Health Benefits: What Science Says
Heart Health & Chronic Disease
- Plant-based diets (even with occasional fish) lower LDL cholesterol and blood sugar levels, reducing risk of heart disease.
- Vegan diets show stronger links to lower blood pressure and weight loss, but both support a healthy diet when focused on whole foods.
Environmental Impact
- Cutting meat consumption slashes greenhouse gas emissions. Veganism has the lowest carbon footprint, but even planet-based diets with fish are greener than meat-heavy ones.
Quick Comparison Chart
Plant Based Vs Vegan Vs Vegetarian
| Category | Plant-Based Diet | Vegetarian Diet | Vegan Diet |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Mostly plant foods, minimal processing. | No meat, but may include dairy products, eggs, honey. | Excludes animal-derived products entirely (food + lifestyle). |
| Animal Products | Occasional (e.g., fish, eggs, dairy). | Dairy, eggs, honey allowed (no meat). | None—avoids meat, dairy, eggs, fish, honey, leather, wool. |
| Ethics | Optional (often driven by health reasons or environmental impact). | Varies (some avoid meat for animal welfare). | Core focus (ethical reasons, animal welfare). |
Final Thoughts: Plant Based Vs Vegan Vs Vegetarian
Whether you’re drawn to plant-based eating for heart health, veganism for animal welfare, or vegetarianism for its simplicity, each diet has unique perks. For a healthy plant-based diet, prioritize food sources like whole grains, fresh fruits, and plant-based meat alternatives.
If you’re unsure, consult a health professional to craft a balanced diet that meets your nutritional needs. Healthy eating can be easy by following different lifestyle choices there are many food products to select from eo ensure optimal health. Weather eating plant-based meals, vegetarian meals, or animal foods, make sure you follow what makes you happy 🙂
Hungry for more? Explore vegan options at your local grocery store or try a vegetarian meal tonight. Your body (and the planet) will thank you.
Sources For Plant Based Vs Vegan Vs Vegetarian:
Harvard Health, HealthLink BC, American Heart Association, National Institutes of Health, World Health Organization, PubMed.
Key Clarification:
- Fish is excluded in vegan diets but sometimes allowed in plant-based diets. Always check labels or ask questions if sustainability or ethics matter to you!




